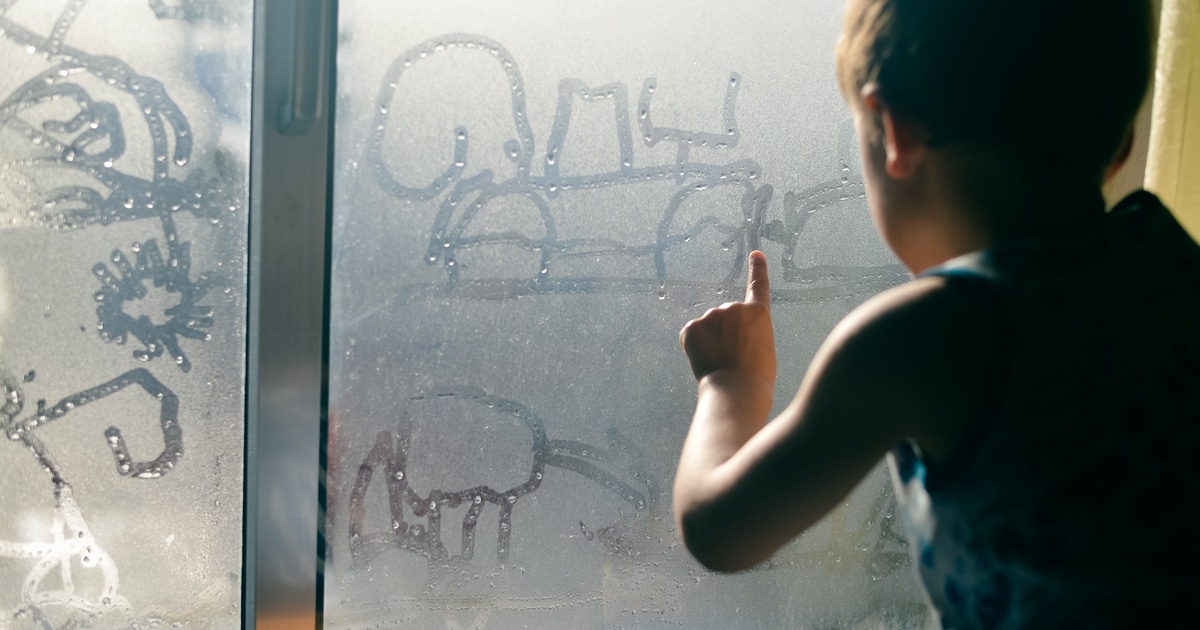
Have you ever noticed water droplets forming on your windows, especially in winter? This is called condensation, and while it might seem harmless, it can lead to mold, damage, and reduced energy efficiency.
In this guide, we’ll explain what condensation resistance is, how it’s measured, and how to choose windows that prevent excess moisture buildup.
What Is Condensation Resistance?
Condensation resistance measures how well a window prevents moisture buildup on the glass surface. The higher the rating, the better the window resists condensation.
How Condensation Resistance Is Measured
- Condensation resistance is rated on a scale from 0 to 100.
- A higher rating means less moisture buildup.
- Energy-efficient windows typically have a condensation resistance rating of 50 or higher.
Typical Condensation Resistance Ratings for Windows
| Window Type | Condensation Resistance Rating | Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Single-Pane Windows | Below 30 | Poor – High condensation risk |
| Standard Double-Pane Windows | 30 – 50 | Moderate – Some condensation control |
| Low-E Double or Triple-Pane Windows | 50 – 70 | Good – Reduces condensation |
| High-Performance Energy-Efficient Windows | 70 – 100 | Excellent – Maximum moisture control |
Why Does Condensation Form on Windows?
Condensation happens when warm indoor air meets a cold window surface, causing moisture in the air to turn into water droplets.
Factors That Increase Condensation
- High Indoor Humidity: More moisture in the air leads to more condensation.
- Poor Window Insulation: Older, single-pane windows get colder and attract moisture.
- Cold Weather: The greater the temperature difference between inside and outside, the more likely condensation forms.
How to Choose Windows with High Condensation Resistance
1. Select Double or Triple-Pane Windows
- More panes reduce heat loss, keeping the inner glass surface warmer.
- Gas-filled windows help improve condensation resistance.
2. Look for Low-E Glass
- Low-E coatings help reduce heat transfer and keep window surfaces warmer.
3. Check the Condensation Resistance Rating
- Look for a rating of 50 or higher for improved moisture control.
4. Choose Vinyl or Fiberglass Frames
- These materials provide better insulation than aluminum or metal frames.
Other Ways to Reduce Window Condensation
Even if you have energy-efficient windows, indoor humidity plays a big role in preventing condensation. Here are some ways to manage moisture levels:
- Use a Dehumidifier: Helps control indoor humidity in winter.
- Ventilate Properly: Run exhaust fans in kitchens and bathrooms.
- Increase Air Circulation: Keep blinds and curtains open to allow airflow around windows.
- Maintain a Consistent Temperature: Avoid extreme indoor temperature fluctuations.
Upgrade to High-Performance Windows
Tired of dealing with condensation? Get a free quote for energy-efficient windows with better condensation resistance.
Learn More About Window Performance
Check out these related guides: